➜ For regular geometric shapes:
For simple, uniformly shaped objects such as cubes, rectangular prisms, cylinders, and spheres, you can use specific geometric formulas to calculate volume. Here are some examples:
- Cube: volume = side length³
- Rectangular prism: volume = length × width × height
- Cylinder: Volume = π × Radius² × Height
- Sphere: Volume = 4/3 × π × Radius³
.
➜ Fluid volume:
The measurement of volumes of liquids or gases requires special equipment such as gas syringes or gas burettes. It must be taken into account that temperature and pressure can influence the volume of substances, especially gases.
The displacement method works as follows: The object to be measured is placed in a container with liquid, and the rise of the liquid level is measured. This rise corresponds to the volume of the object. Archimedes’ principle states that the volume of an irregularly shaped object can be determined by the amount of water it displaces when immersed. By measuring the change in water level before and after immersion of the object, you can calculate its volume.
For objects with irregular shapes, so-called free shapes, such as adhesive beads, weld beads, displacement methods cannot be used to measure a volume.
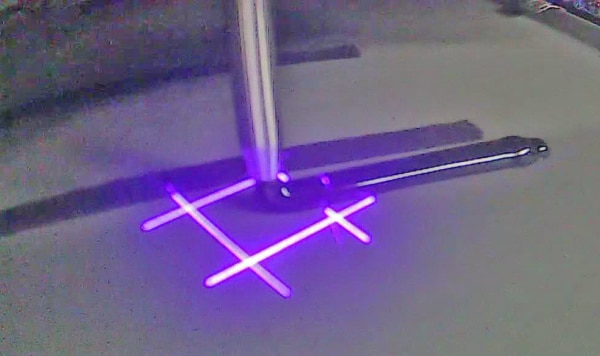
➜ Computer-aided techniques for volume measurement
In today’s world, computer-aided methods such as 3D laser line triangulation sensors and image processing software are increasingly being used to precisely measure the volume of complex shapes. These technologies allow the object to be digitally captured and the volume to be calculated using computational methods. 3D measurement enables accurate determination of the smallest enveloping surface of objects.3D laser line triangulation sensors can capture object contours from all sides in three dimensions within seconds.
Laser triangulation is an advanced method for distance measurement and shape determination of objects based on the principles of geometry and optics. This method uses triangulation to calculate the distance to an object based on the angles and known dimensions of a triangle consisting of a light source, a sensor and the object to be measured.
➜ The structure works as follows:
- A laser light source projects a line onto the object to be measured, which is reflected from the surface.
- A special camera sensor captures the diffusely reflected laser light at a defined angle. The positions of the points on the laser line are calculated in height (z).
By knowing the fixed distance between laser source and sensor as well as the angle of incidence of the laser light on the sensor, the points of a laser line can be calculated in height (z) and width (x). In this way, a 2-dimensional profile is created. Several of these profiles, taken at a fixed distance from each other, result in a 3D point cloud. These calculations are performed in the 3D laser line triangulation sensor using trigonometric principles.
➜ The accuracy of these measurements depends on several factors:
- Angle measurement precision
- Laser light wavelength
- Quality of the optics and the resolution of the sensor
Calibration processes are used to ensure accurate results and to account for potential errors or deviations in the system.
However, it is important to note that 3D laser line triangulation sensors are only suitable for measuring solids.