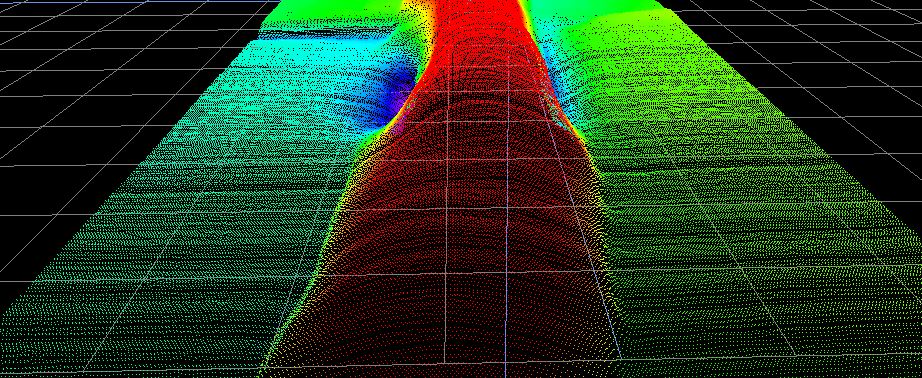
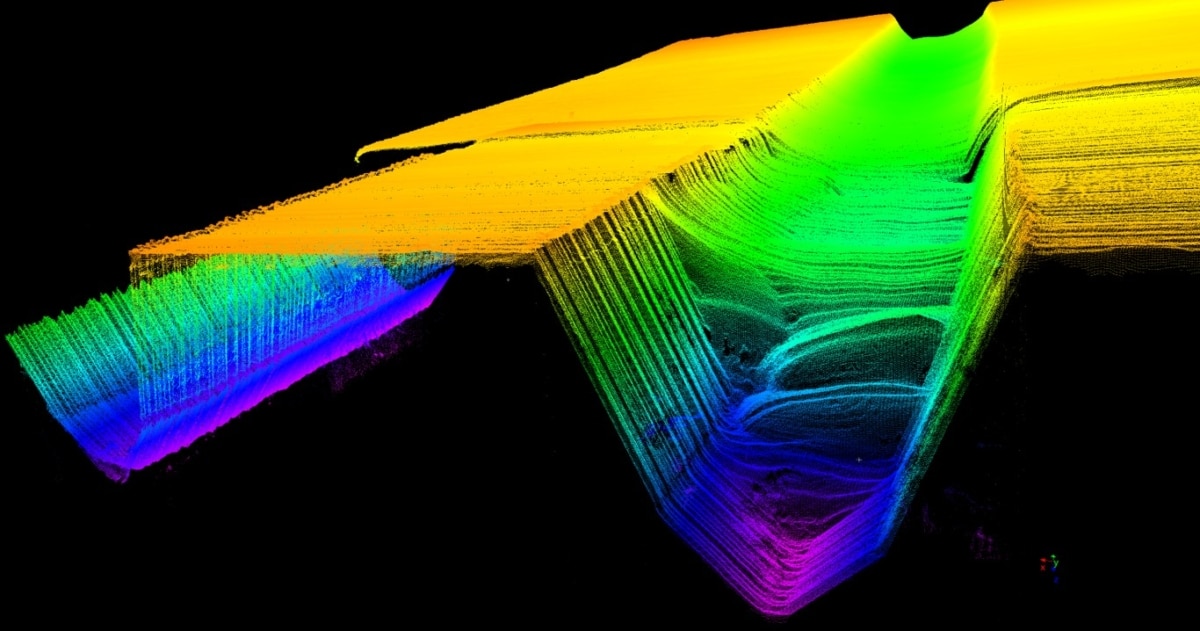
Weld seam guidance
In a weld seam guide, the welding torch is brought into the optimum position along the welding gap between two components. The gap is continuously scanned with a laser profile scanner running ahead and the optimum position for the torch is calculated.
When the torch reaches the measured position, it is moved to the optimum position at this point by means of the motor axes or a robot. This allows web and component tolerances and heat distortion to be compensated for during welding.
Definition weld seam guide
Welding seam guidance is a technique in which the welding torch and the welding wire are precisely positioned along the welding gap. When aligning the weld metal to the gap, various tolerances play a role that can influence the dimensions, geometry and position of the weld gap in space.
Even if the gap is laid out straight in the design, in practice it can be uneven and show variations in the width and height of the opposite edges. These variations can be caused by various factors such as the type of fixture or the dead weight of the components.
During the welding process, another effect occurs that can hardly be compensated for by design measures: Namely, thermal distortion. To compensate for these effects, the technique of laser weld seam tracking was developed.